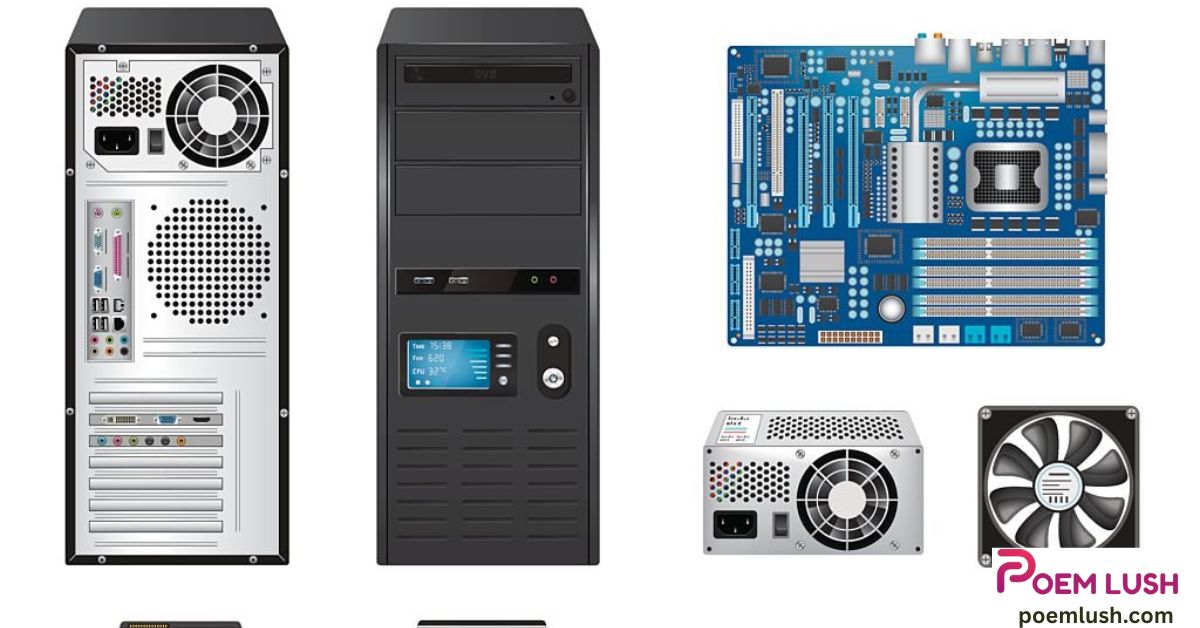
Computer Parts Images Understanding your computer from the inside out can be a game changer—whether you’re building a custom PC, upgrading hardware, or simply trying to troubleshoot. This guide is packed with high-resolution computer parts images, detailed explanations, practical insights, and visual references that help you confidently identify, understand, and use each part of your computer. Computer Parts Images
From processors to cooling fans, this post dives deep into every essential internal component. Whether you’re a beginner or a curious tech enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will give you the edge you need. Computer Parts Images
What Are Computer Parts?

Computer parts are the physical components that make up a computer system. These are also called hardware components and include everything inside your computer’s case. Unlike software, which is intangible, hardware can be touched, replaced, and upgraded. Computer Parts Images
There are two broad categories of computer hardware:
- Internal components: The core parts inside the system that perform computing tasks (CPU, RAM, motherboard, etc.)
- External components: Peripherals like monitors, keyboards, and printers
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the heart of your computer. It performs calculations, runs programs, and handles instructions. When you open a file, click a button, or launch a game, the CPU makes it happen. Computer Parts Images
Key Facts
- Known as the brain of the computer
- Most common manufacturers: Intel and AMD
- Modern CPUs have multiple cores (quad-core, hexa-core, octa-core)
- Installed directly into the CPU socket on the motherboard
What It Looks Like
- Typically a small, square chip with gold contacts on the bottom
- Comes with a metal lid (called an IHS) on top
Visual Tip
The pins on AMD CPUs are on the processor. For Intel, the pins are in the socket.
“A good CPU ensures fast performance in everything from video editing to multitasking.” — TechRadar
Common CPU Terms
- Clock speed: Measured in GHz, higher = faster
- Cores/Threads: More cores = more tasks handled at once
- Cache memory: Faster than RAM, used for quick data access
Motherboard Circuit
The motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in your computer. It’s where all other components connect.
Purpose of the Motherboard
- Connects CPU, GPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals
- Routes power and data between components
What It Looks Like
- Large flat board with many slots and connectors
Key Components on the Board
- CPU socket
- RAM slots (usually 2 to 4)
- PCIe slots for GPUs
- SATA connectors for storage drives
- Power connectors from PSU
- Chipsets that control I/O functions
Variants
| Form Factor | Use Case |
| ATX | Full-sized, for gaming or powerful PCs |
| Micro-ATX | Mid-sized, fits smaller cases |
| Mini-ITX | Small builds like HTPCs |
“The motherboard is the unsung hero that glues the entire system together.”
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM (Random Access Memory) stores data your system uses actively. Unlike hard drives or SSDs, RAM is fast but volatile—it loses data when power is off.
Why RAM Matters
- Speeds up tasks like browsing, gaming, or editing
- More RAM = more multitasking capability
What It Looks Like
- Long, thin sticks with gold pins
- Inserted into vertical RAM slots on the motherboard
Quick Tips
- Always match RAM speed to motherboard compatibility
- Dual-channel RAM improves performance
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) renders images, videos, and animations. It’s essential for gaming, 3D rendering, and even AI tasks.
GPU Types
- Integrated GPU: Built into the CPU (less powerful)
- Dedicated GPU: Separate card, more powerful
What It Looks Like
- Usually the largest card in the system
- Includes fans, heatsinks, and PCIe connector
Top Brands
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX series
- AMD Radeon RX series
Slot Type
- Installs into a PCIe x16 slot
Pro Tip
For gaming, look for GPUs with at least 8GB of VRAM.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) vs Solid State Drive (SSD)
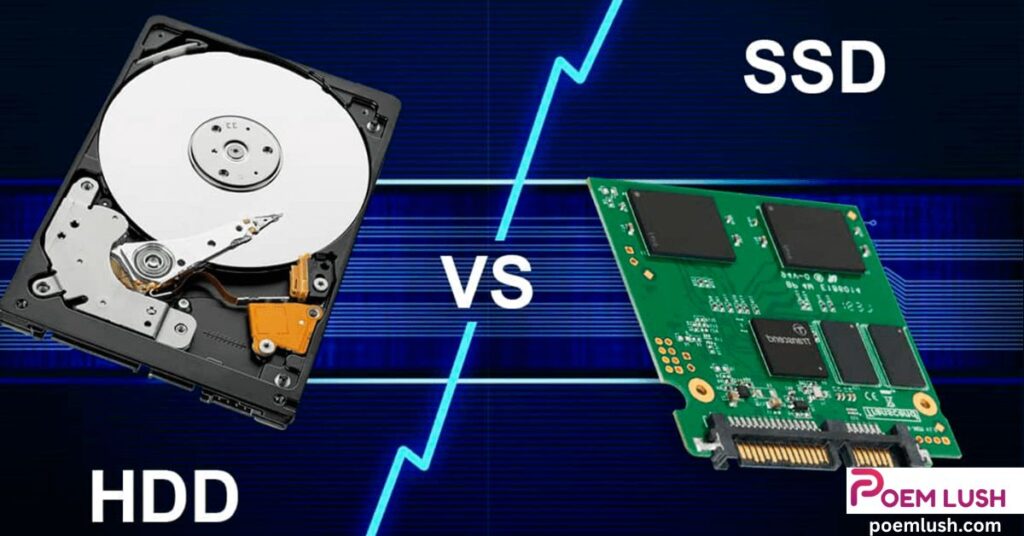
Both HDDs and SSDs store files, operating systems, and software.
What They Look Like
- HDD: Metal box, larger and heavier
- SSD: Slimmer, lighter, often rectangular
Key Differences
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
| Speed | Slower | Much faster |
| Durability | Fragile | Shock-resistant |
| Noise | Audible spinning | Silent |
| Cost | Cheaper | More expensive per GB |
“For best performance, use SSD for your operating system and HDD for storage.”
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The PSU converts electricity from your wall outlet into usable power for your PC components.
Why It’s Important
- Delivers stable voltage
- Prevents power surges and hardware damage
Common Wattage Ratings
- Basic PC: 450W
- Gaming PC: 650W – 850W
- Workstations: 1000W+
Computer Cooling Fan
Fans keep your computer from overheating by circulating air.
Types of Fans
- Case fans: Move air in/out of the case
- CPU fan: Sits on top of the CPU heatsink
- GPU fans: Attached directly to graphics cards
What They Look Like
- Plastic blades, usually 80mm to 140mm
Airflow Diagram
[IN] —> [CPU/GPU] —> [OUT]
“Airflow management is crucial to system longevity.”
Optical Drive Media
Though declining in use, optical drives read/write CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.
What It Looks Like
- Tray-loading or slot-loading
- Installed in front-facing 5.25″ bay
Still Relevant?
- Useful for older media, software, or movies
- Can be external USB-powered
Network Interface Card (NIC)
The NIC connects your computer to the internet.
NIC Types
- Ethernet NIC: Wired connection (RJ45 port)
- Wi-Fi NIC: Wireless adapter (PCIe or USB)
What It Looks Like
- Small circuit board with a port or antenna
Pro Tip
For stable gaming or streaming, always prefer wired Ethernet over Wi-Fi.
Memory Card Reader
Used to access data from SD cards, microSD cards, and similar.
What It Looks Like
- Front panel slot or external USB box
Common Uses
- Transferring photos from cameras
- Accessing phone storage
- Reading security camera footage
Other Crucial Internal Components
Besides the major parts, here are other key pieces inside your PC:
- CMOS Battery: Stores BIOS settings
- Heatsinks: Passive cooling for CPU/GPU
- Expansion Cards: Audio, capture, RAID cards
- SATA/Molex Cables: Power and data transmission
“Even the smallest component has a big role in stability and performance.”
External Computer Parts (Quick Visual Reference)
These aren’t inside the case, but they matter too.
- Monitor
- Keyboard & Mouse
- Speakers or Headphones
- Webcam
- USB Ports / Audio Jacks
How to Identify Computer Parts Inside Your PC
Visual Inspection Tips
- Look for labels and logos on each part
- Trace cables to see connections
- Use a flashlight and anti-static precautions
Software Tools
- CPU-Z (CPU, RAM, motherboard info)
- Speccy (full system overview)
Choosing the Right Computer Parts for Your Build

When building or upgrading, compatibility is key.
Compatibility Checklist
- CPU socket must match motherboard
- RAM speed must match motherboard specs
- PSU must support GPU power requirements
Common Mistakes
- Buying the wrong size case
- Not enough wattage on PSU
- Mismatched RAM speeds
Downloadable Resources
- ✅ [Printable Chart]: Computer Parts and Functions
- ✅ [PDF Guide]: Visual Computer Parts Dictionary
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding each computer part visually empowers you to make smarter tech decisions. Whether you’re building, upgrading, or troubleshooting, these computer parts images and deep knowledge give you a huge advantage.
Be sure to bookmark this guide, explore your own PC, and feel free to ask questions or share your experiences.
FAQs
What’s the most important part of a computer?
The CPU, but it must work with a good GPU, RAM, and SSD.
How do I know what parts are inside my PC?
Use visual inspection + tools like Speccy or CPU-Z.
Is SSD better than HDD?
Yes. SSDs are faster, quieter, and more durable.
Can I upgrade just my RAM?
Yes, but check motherboard limits and slot availability.


